Java集合结构学习
源码类图
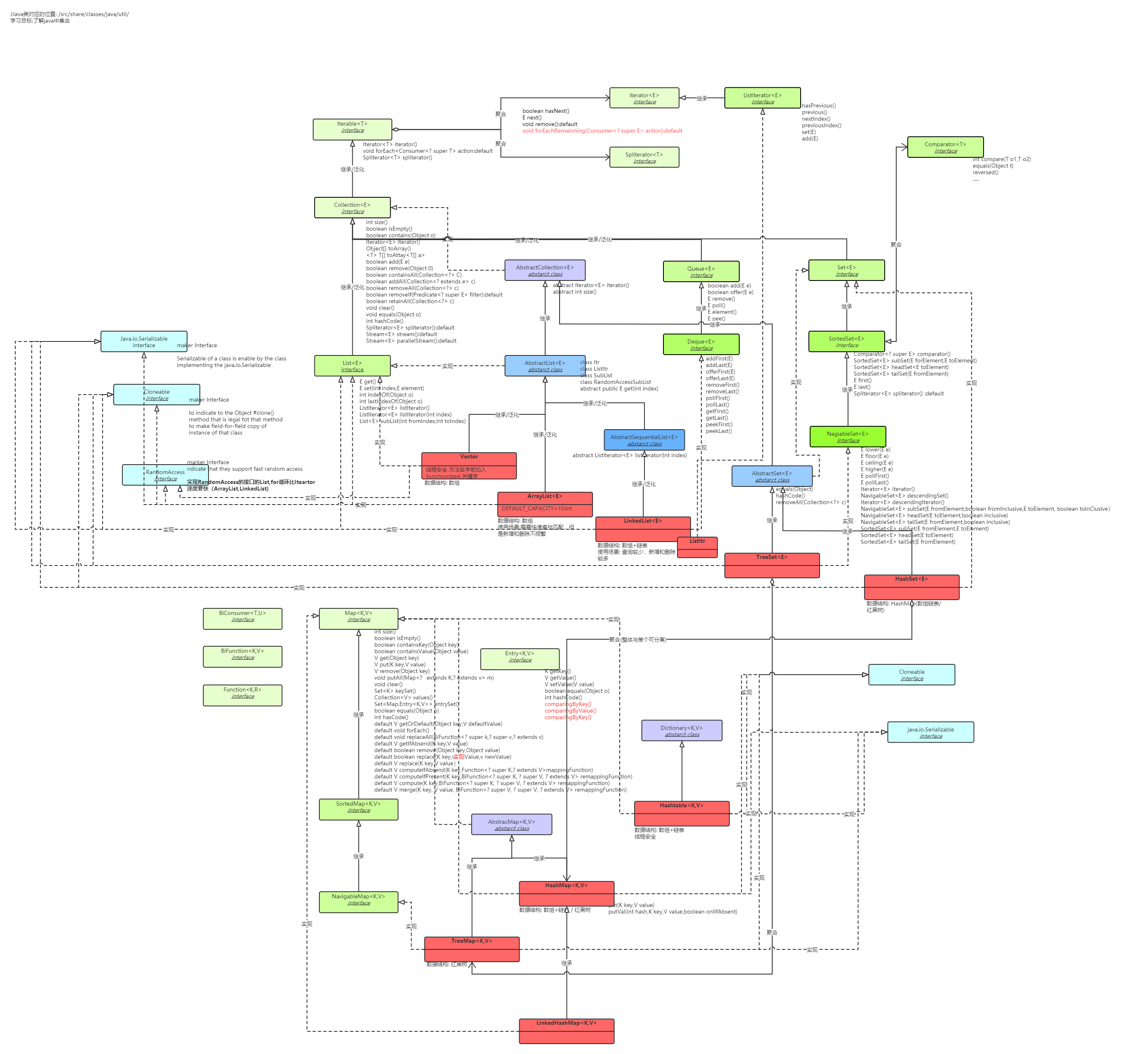
源码学习
1.List
1.1 Vector
Vector实现是数组,默认空构造方法长度为10,也可以根据传入initialCapacity
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
public Vector() {
this(10);
}Vector使用时
允许添加value是null
size(),isEmpty(),get(index),set(int,E),add() 方法的执行时间复杂度O(1),注意这里的关键字Synchronized
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29public synchronized int size() {
return elementCount;
}
public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {
return elementCount == 0;
}
public synchronized E get(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return elementData(index);
}
public synchronized E set(int index, E element) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}线程是否安全? 肯定的哈,这么多synchronized
扩容:看到这里发现了个”+”,原来是2倍
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11grow(minCapacity);
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}扩容本质:
1
Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity)Vector看起来平常很少用哈!!!
1.2 ArrayList
ArrayList实现是一个数组,默认长度10,size(int)表示长度。代码摘选如下:
1
2
3private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACTITY=10;//默认长度
transient Object[] elementData;//基本实现数组
private int size;//大小ArrayList 使用时
- 允许添加value是null的值
- size(),isEmpty(),get(index),set(),add()方法的执行时间复杂度均为O(1),这里的时间复杂度表示访问单个元素时,因为访问只需要一条指令。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
//返回List的大小实现
public int size() {
return size;
}
//返回List是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
//根据index返回value
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index); // 检查是否越界
return elementData(index);// 返回ArrayList的elementData数组index位置的元素
}
//设置index的value
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index); // 检查是否越界
E oldValue = elementData(index);// 调用elementData(index)获取到当前位置的
elementData[index] = element; // 将element赋值到ArrayList的elementData数组的第index位置
return oldValue;
}
//添加一个值(在添加时未进行null判断,所有ArrayLsit是允许空值存在)
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // 扩容 // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e; // 将e赋值给elementData的size+1的位置
return true;
}
线程是否安全? 不安全,这里并未看到对方法或者全局变量使用synchronized关键字。以及size并未使用volatile修饰
- 扩容规则
- 扩容大小为原大小的1.5倍,后使用Arrays.copyof(old,new)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 获取到ArrayList中elementData数组的内存空间长度
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);// 扩容至原来的1.5倍
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)//若预设值大于默认的最大值检查是否溢出
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);// 并将elementData的数据复制到新的内存空间
} - 扩容的本质:
1
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, newElementData, 0,Math.min(elementData.length,newCapacity))
- 扩容大小为原大小的1.5倍,后使用Arrays.copyof(old,new)
- 使用总结
- ArrayList删除时间复杂度为O(1),且允许删除null值
- ArrayList全局变量且多线程使用时,存在问题.作为局部变量,放心用吧!!!
- 可以使用的Collections#synchronizedList保证线程安全
- 使用ArrayList时为了便面多次copy的过程,可以在初始化时指定固定大小
1.2 LinkedList
LinkedList底层数据结构是一个双向链表,既然是双向链表。可以被当作栈,队列。非线程安全
1
2
3transient int size=0;
transient Node<E> first;//transient 防止序列化
transient Node<E> last;LinkedList 方法实现(这里只对思路和public方法记录下)
- 头节点插入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11private void linkFirst(E e){
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null,e,f);
first = newNode;
if(f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
} - 尾节点插入(不做笔记)
- 在succ节点前插入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11void linkBefore(E e,Node<E> succ){
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;//保存前一个节点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred,e,succ);//创建一个新的节点
succ.prev = newNode;//succ的前节点设置为newNode
if(pred==null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
} - 删除非空节点
- 获取首节点,并且返回头节点值
1
2
3
4
5
6public E getFirst(){
final Node<E> f = first;
if(f==null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item
} - 获取尾节点,返回存储的元素值
- 在头节点插入
- 判断元素是否包含
1
2
3
4
5public boolean contains(Object o){
return indexOf(o)!=-1;
}
```
- 查询操作返回对应的Indexpublic int indexOf(Object o){ int index = 0; if(o==null){ for(Node<E> x= first;x!=null;x=x.next){ if(x.itme==null) return index; index++; } }else{ for(Node<E> x= first;x!=null;x=x.next){ if(o.equals(x.item)) return index; index++; } } }static final int DEFAULT_ININIAL_CAPCITY=1<<4;//默认161
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9- 获取头节点 peeK()
- 获取并删除头节点 poll()
- 等等(这些方法的实现还是比较简单,都是比较常规的操作)
### 2.Map
#### 2.1 HashMap
- [在线查看](https://github.com/wupeixuan/JDKSourceCode1.8/blob/master/src/java/util/HashMap.java)
- HashMap底层数据结构
数组+链表+红黑树,当链表的长度大于等于8时,链表会转换成为红黑树,当红黑树的大小小于等于6时,红黑树会转换成为链表。
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY =1<<30;//最大
transient Node<K,V>[] table;//存储数组的元素
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>{}//红黑树的实现
static class Node<K, V> implements Map.Entry<K, V>{}//链表的节点
```
- 头节点插入
2.1.1 LinkedHashMap
2.2 TreeMap
2.3 HashTable
2.4 EnumMap
3.Set
3.1 HashSet
3.1.1 LinkedHashSet
3.2 TreeSet
SortedSet
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!